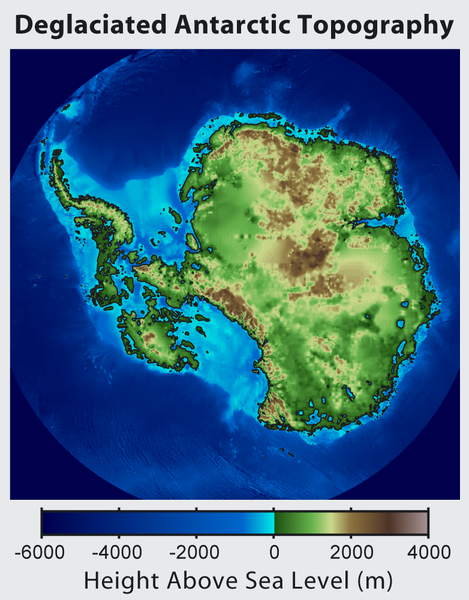
Файл:Antarctica Without Ice Sheet.png
Памер прагляду: 469 × 600 піксэлаў. Іншыя разрозьненьні: 188 × 240 піксэлаў | 375 × 480 піксэлаў | 782 × 1000 піксэлаў.
Арыгінальны файл (782 × 1000 піксэляў, памер файла: 675 кб, тып MIME: image/png)
Гісторыя файла
Націсьніце на дату/час, каб паглядзець, як тады выглядаў файл.
| Дата і час | Мініятура | Памеры | Удзельнік | Камэнтар | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| цяперашняя | 19:56, 16 чэрвеня 2015 |  | 782 × 1000 (675 кб) | Szczureq | larger image |
| 08:57, 10 кастрычніка 2012 |  | 469 × 600 (316 кб) | Strannik27 | User created page with UploadWizard |
Выкарыстаньне файла
Наступная старонка выкарыстоўвае гэты файл:
Глябальнае выкарыстаньне файла
Гэты файл выкарыстоўваецца ў наступных вікі:
- Выкарыстаньне ў ar.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ast.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ban.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ba.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў be.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў br.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў bxr.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ca.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў cs.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў de.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў en.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў es.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў es.wikibooks.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў fr.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў id.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў it.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ja.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ka.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў kn.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў la.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў mn.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў nl.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў no.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў pl.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў ru.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў tg.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў tr.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў uk.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў zh.wikipedia.org
- Выкарыстаньне ў zu.wikipedia.org

